Detecting gravitational waves
More about gravitational wave detectors on earth and in space
Climate research with gravitational wave technology
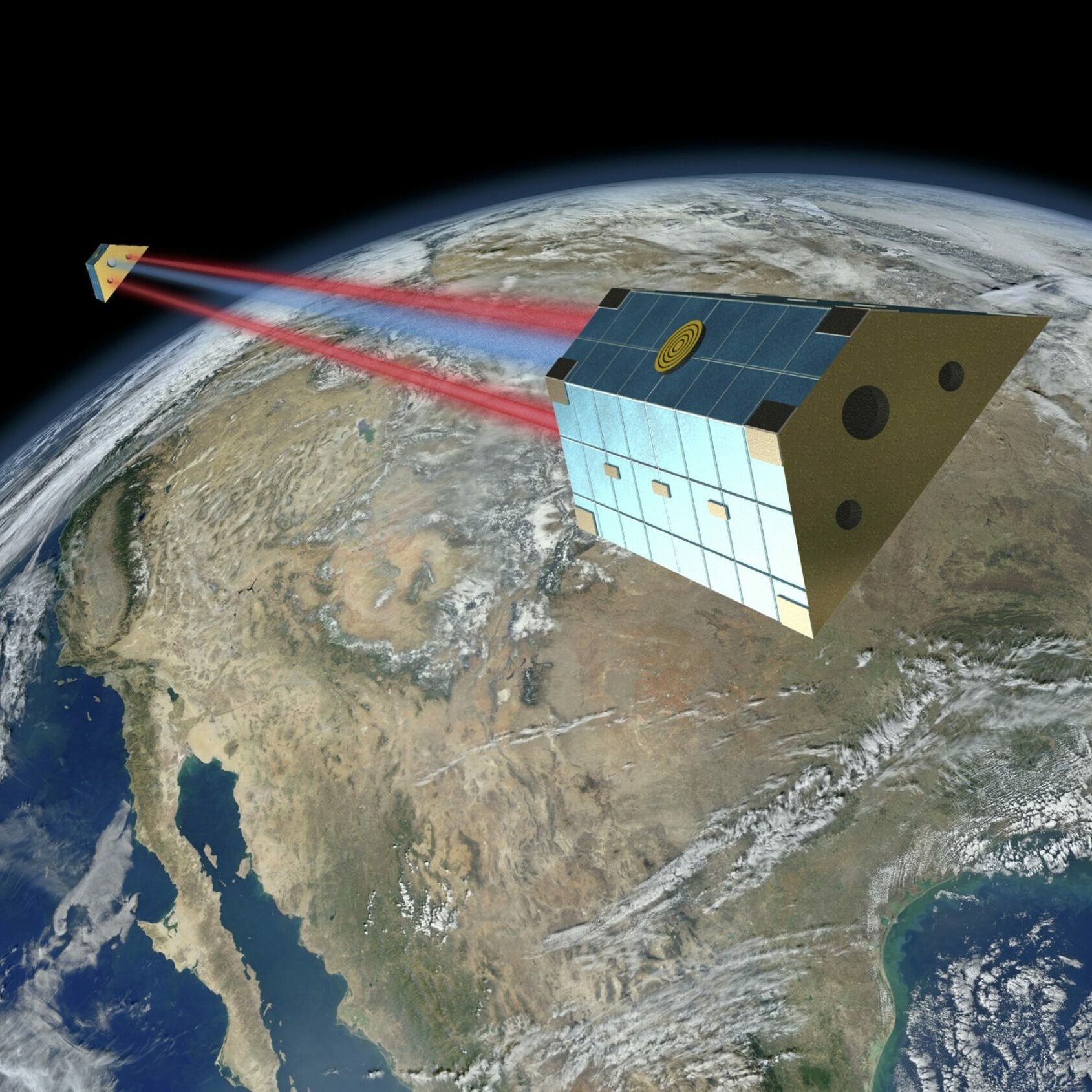
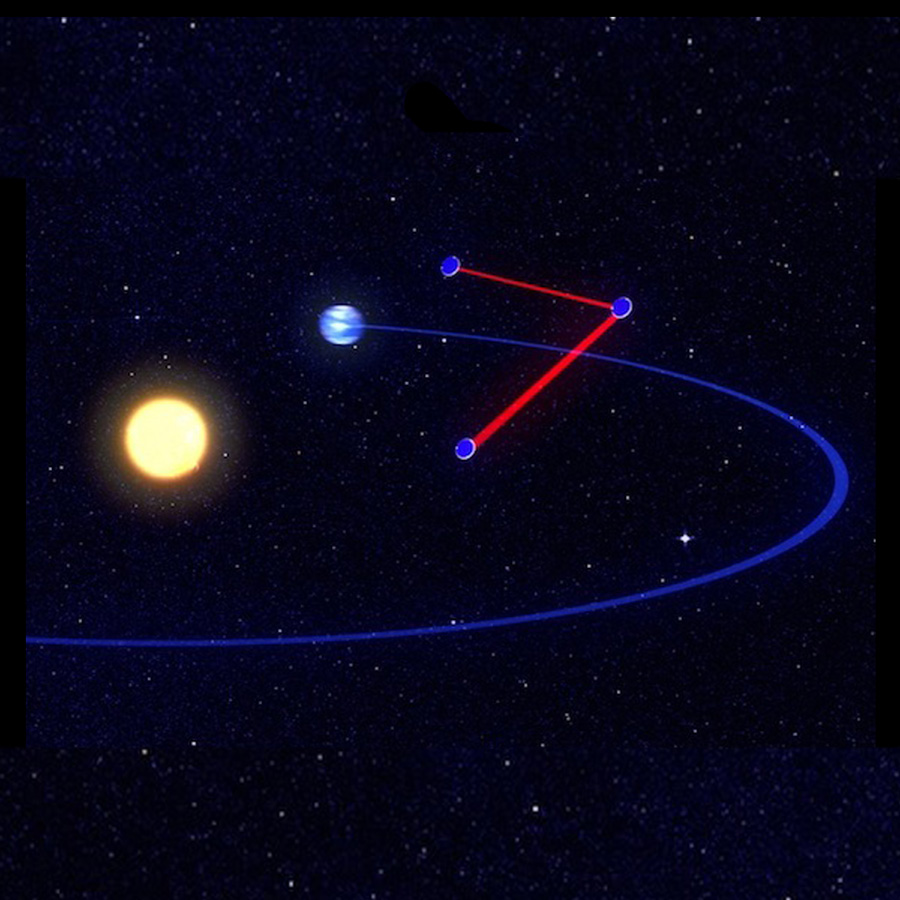
The two GRACE Follow-On satellites have been measuring the Earth’s gravitational field since mid-2018 to obtain important data for geophysics and climate research. On board is a laser interferometer that will serve as a model for future satellite missions and represents a step toward the LISA gravitational wave observatory.
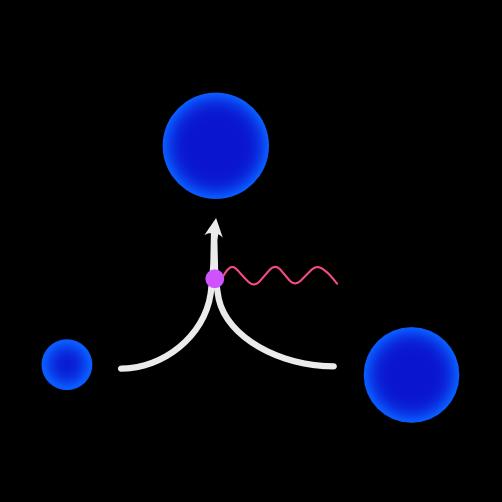
Gravitational wave detectors find 56 potential cosmic collisions
During collaborative measurement campaigns, so-called observation runs, the worldwide gravitational wave detector network listens for signals from space. During the third observation run “O3”, which started on April 1st, 2019, the LIGO detectors (USA), Virgo (Italy), and GEO600 (Germany) recorded a range of promising signals.
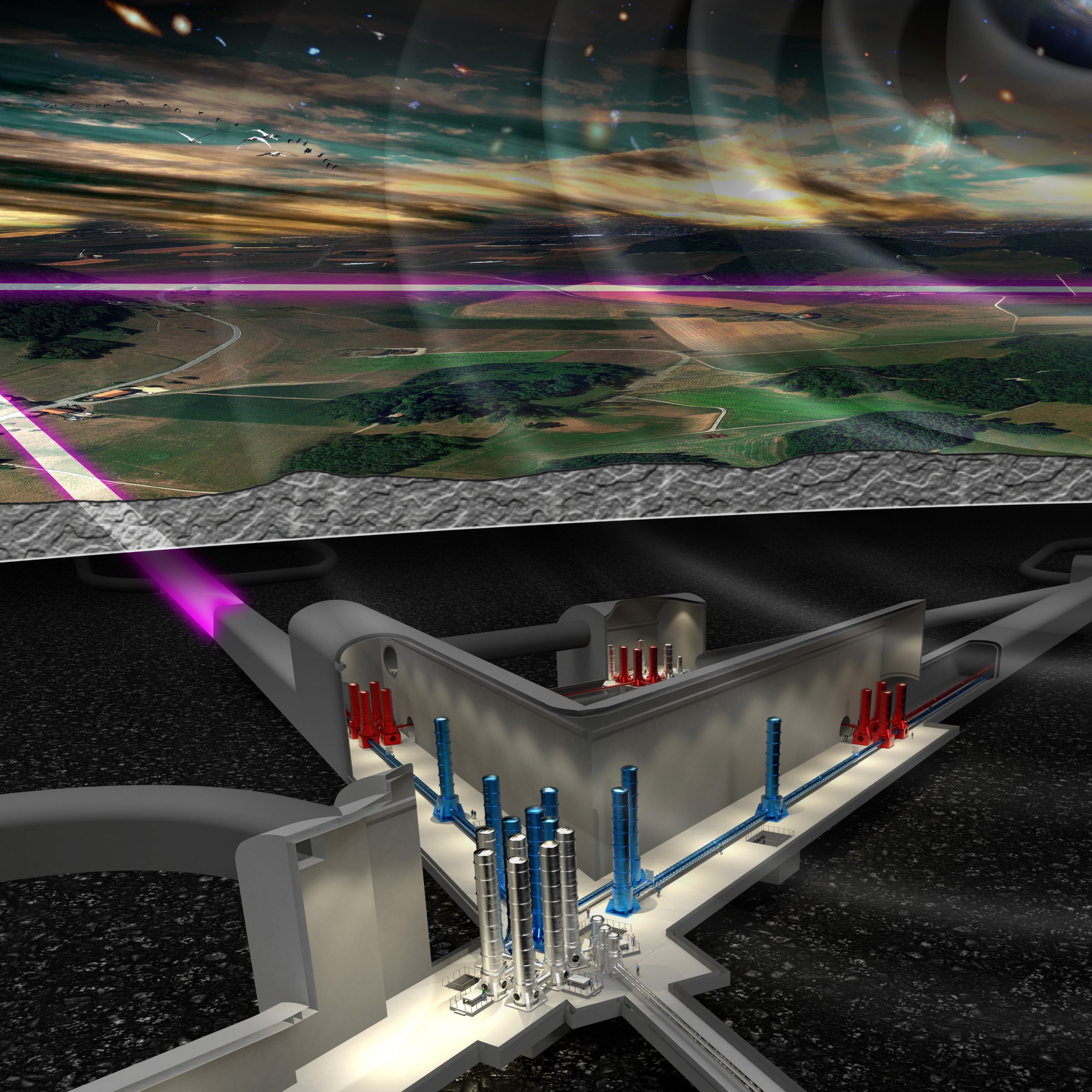
Third-generation gravitational-wave detectors
Starting in the 2030s, third-generation gravitational-wave observatories will eavesdrop on space. They are many times more sensitive than current detectors and could thus provide a range of new insights into the invisible side of the universe.
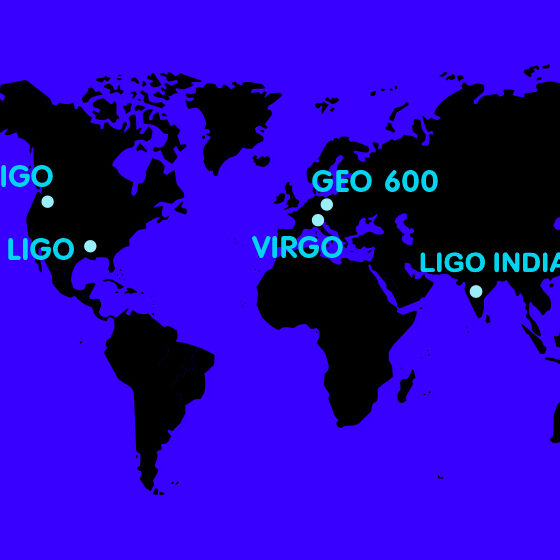
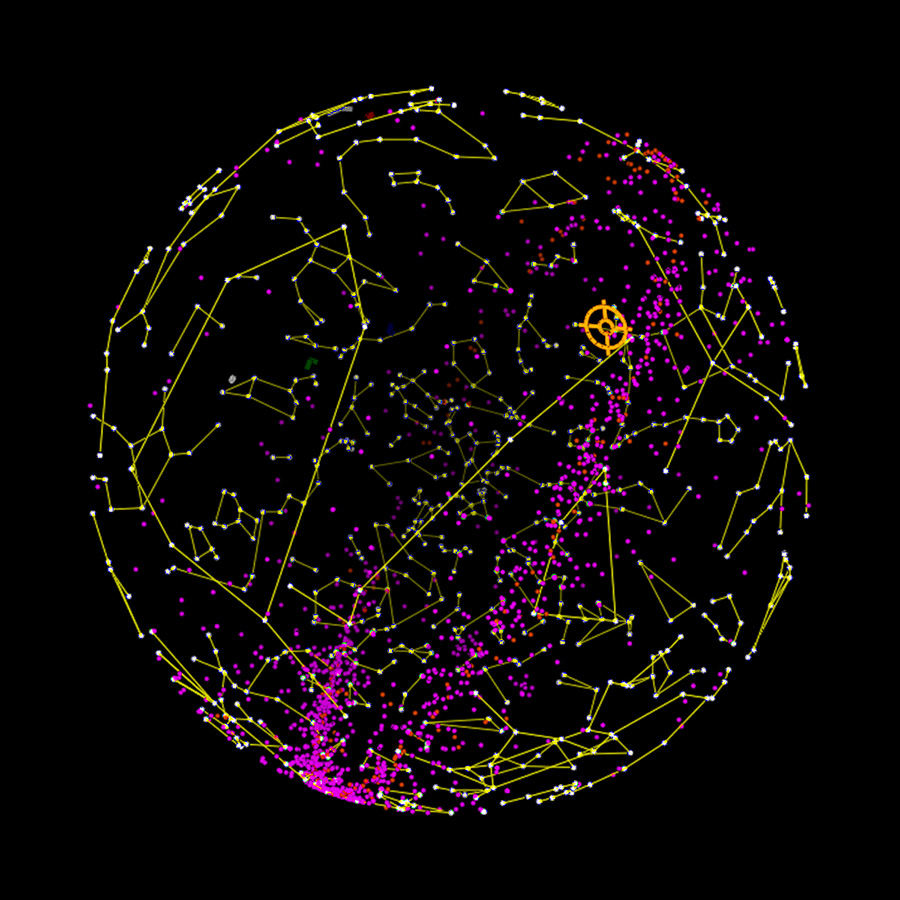
Listening posts around the globe
Overview of the gravitational wave detectors currently operational, or under construction
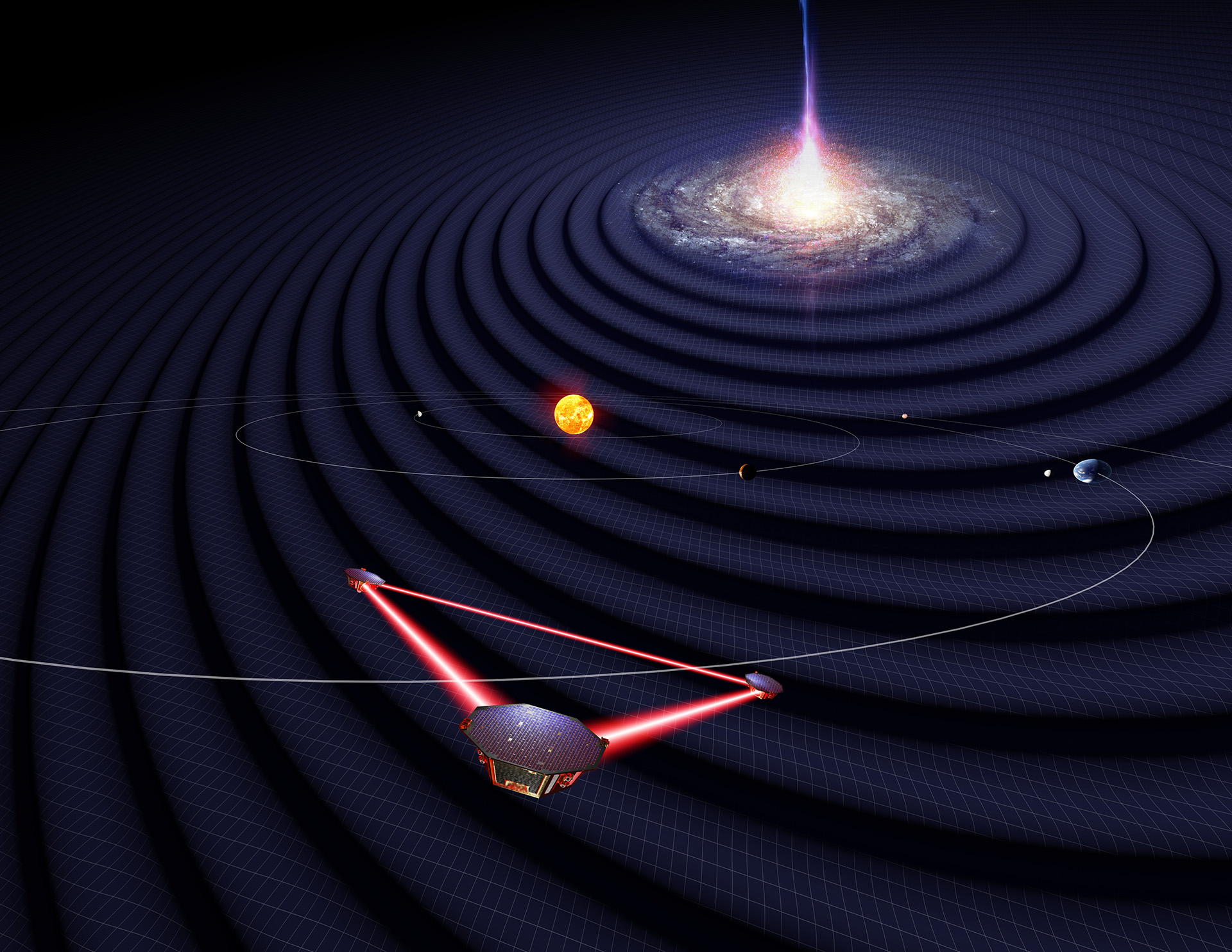
Observing gravitational waves in space with LISA
In 2035, the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is scheduled to be launched into space as a mission of the European Space Agency (ESA). It will observe previously inaccessible gravitational waves from a large range of new sources.
Einstein@Home – gravitational waves for everybody
Information on how you personally can help with the search for gravitational wave – by donating processing time on your private computer
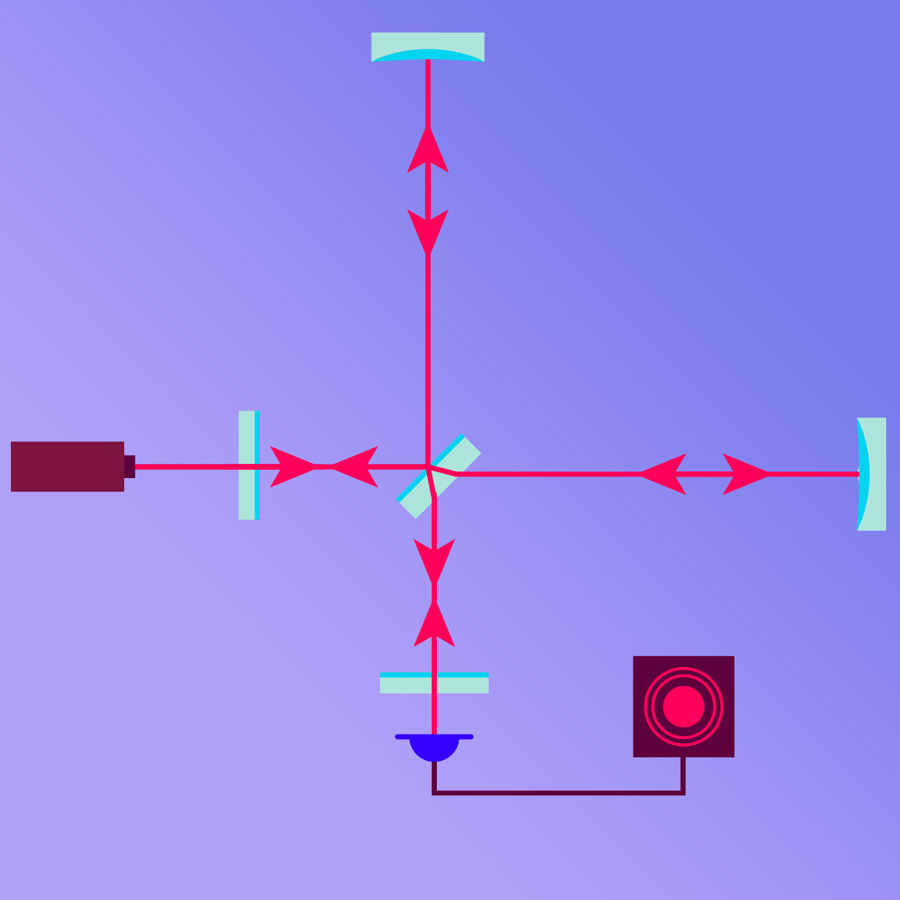
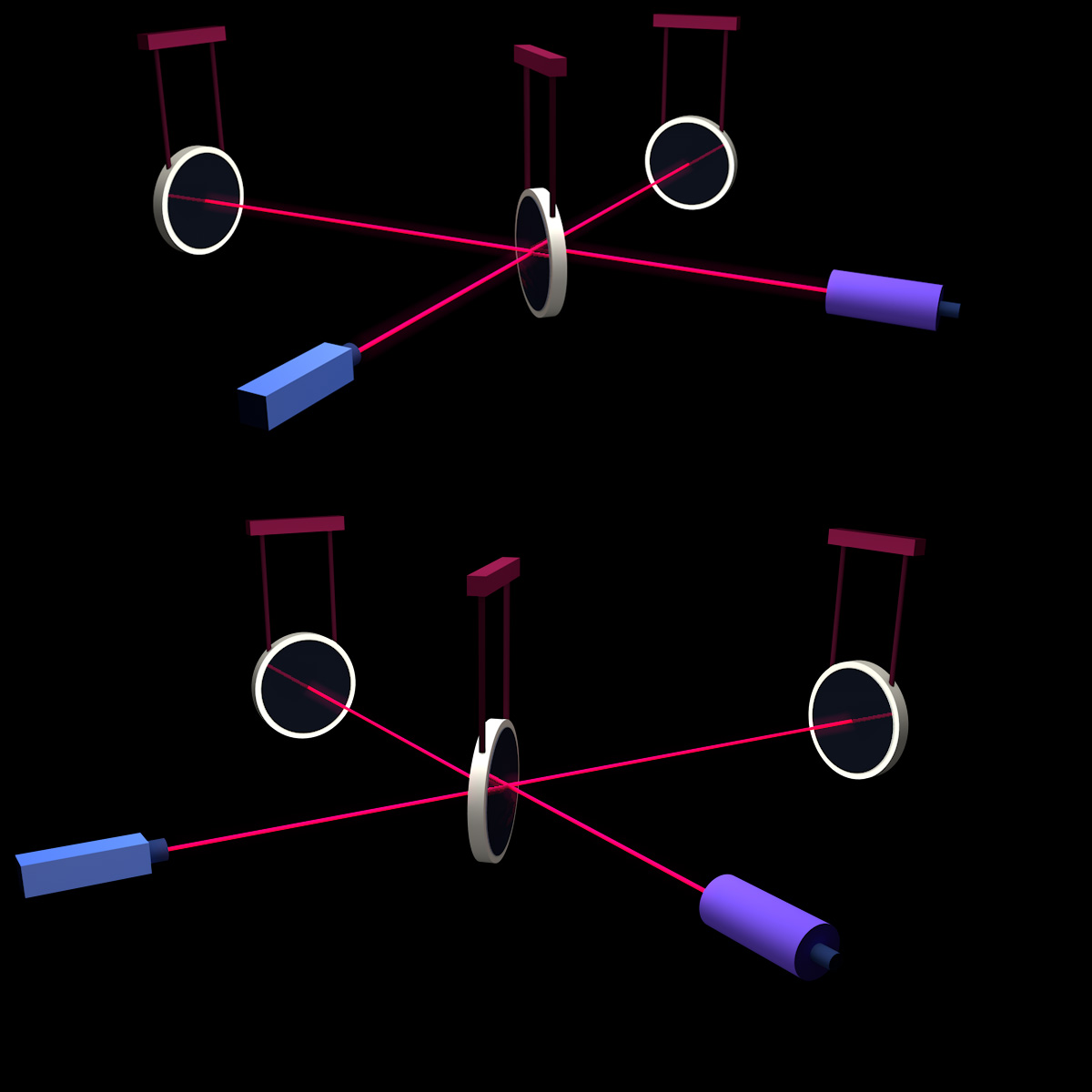
Catching the wave with light
Some information on how interferometric detectors such as LIGO or GEO600 work
Small vibrations
Some information on how the vintage models among gravitational wave detectors work – resonant detectors
LISA – Hunting waves in space
Information about the latest version of the most ambitious gravitational wave project – a detector in space.
Interferometric gravitational wave detectors
All modern gravitational wave detectors are based on the principle of a Michelson interferometer. But how exactly does it work?