Special relativity
The basics and some applications of special relativity: Relativistic nobel prizes, the concept of relativity, E-equals-m-c-squared, time dilation and the (in)famous twins.
This page contains an overview of those of our Spotlights on Relativity dealing with the foundations and applications of the special theory of relativity. In the category Basics, there is a text dealing with the meaning of “relativity”; under the heading Time, you will find texts dealing with simultaneity, time dilation and the famous travelling twins, while under Energy and mass, there is some information about Einstein’s best-known formula. Under Miscellaneous, you will find a text describing all relativity-related Nobel prizes.
A brief overview of special relativity can be found in our introduction Elementary Einstein, in particular in the chapter Special relativity.
Basics
Waves, motion and frequency: the Doppler effect
How motion influences waves, or other kinds of ever-repeating signals, in classical physics and in special relativity.
The dialectic of relativity
How relativity can reconcile statements that, at first glance, appear to be contradictory
Special relativity and time
More about simultaneity, time dilation and the famous case of the travelling twin
From light clocks to time dilation
A simple thought experiment with light clocks – clocks in which light keeps stroke – allows the derivation of time dilation.
The definition of “now”
Why it is necessary to define simultaneity, and how best to go about defining it.
Time dilation on the road
How you can picture the relativity of simultaneity and time dilation, using a simple geometric analogy
The case of the travelling twins
Why the so-called “twin paradox” isn’t really a paradox
Twins on the road
How one can picture the situation of the travelling twin, using a simple geometric analogy
Energy and mass
Some background information about the most famous formula in all of physics
Is the whole the sum of its parts?
Why Einstein’s famous formula tells us that the whole, as far as mass is concerned, is often less than the sum of its parts
From E=mc² to the atomic bomb
The subtle connections between Einstein’s formula, nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
Miscellaneous
Einstein’s Nobel heritage
An overview of Nobel prizes connected with relativistic physics
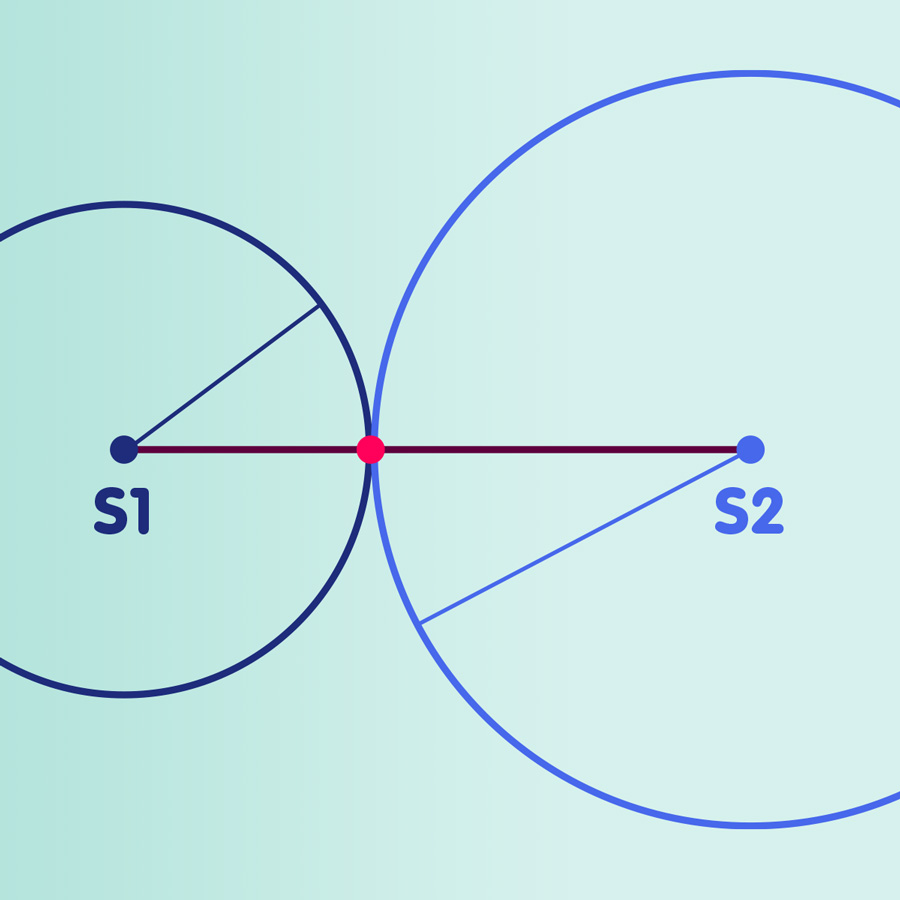
Relativity and satellite navigation
How to determine your position using radio signals and satellites – and what the theories of relativity have to do with it
Time determination with radio signals – from radio-controlled clocks to satellite navigation
How to determine the exact time anytime and anywhere with the help of a radio receiver (and some additional information)
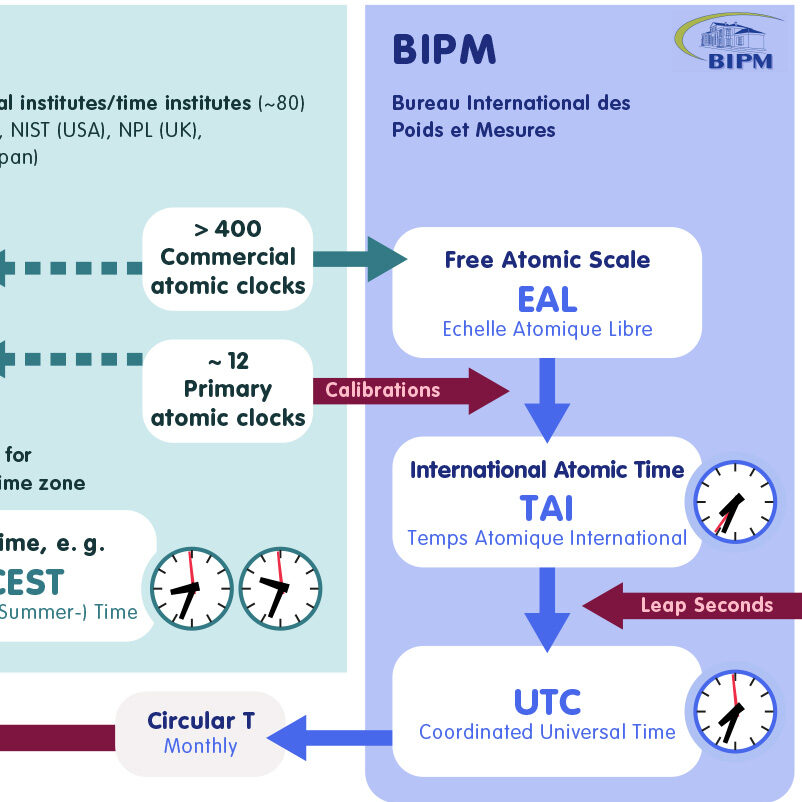
How time is made
How the internationally valid coordinated universal time UTC is determined – and what role the theory of relativity plays in it