Gravitational wave sources
Continuous gravitational waves
A vast population of a hundred million stellar remnants is hidden in the depths of our Galaxy. While we may never observe them in the electromagnetic spectrum, we might discover them through their gravitational-wave emission.
First measurement of gravitational waves of colliding neutron stars
Not only merging black holes, but also neutron star pairs emit gravitational waves.
Gravitational wave detectors find 56 potential cosmic collisions
During collaborative measurement campaigns, so-called observation runs, the worldwide gravitational wave detector network listens for signals from space. During the third observation run “O3”, which started on April 1st, 2019, the LIGO detectors (USA), Virgo (Italy), and GEO600 (Germany) recorded a range of promising signals.
The first catalogue of cosmic collisions
From the data of the first two observation runs of LIGO and Virgo, the scientists have created a first catalogue of cosmic collisions. The catalogue contains gravitational wave signals from ten pairs of merging black holes and one pair of neutron stars.
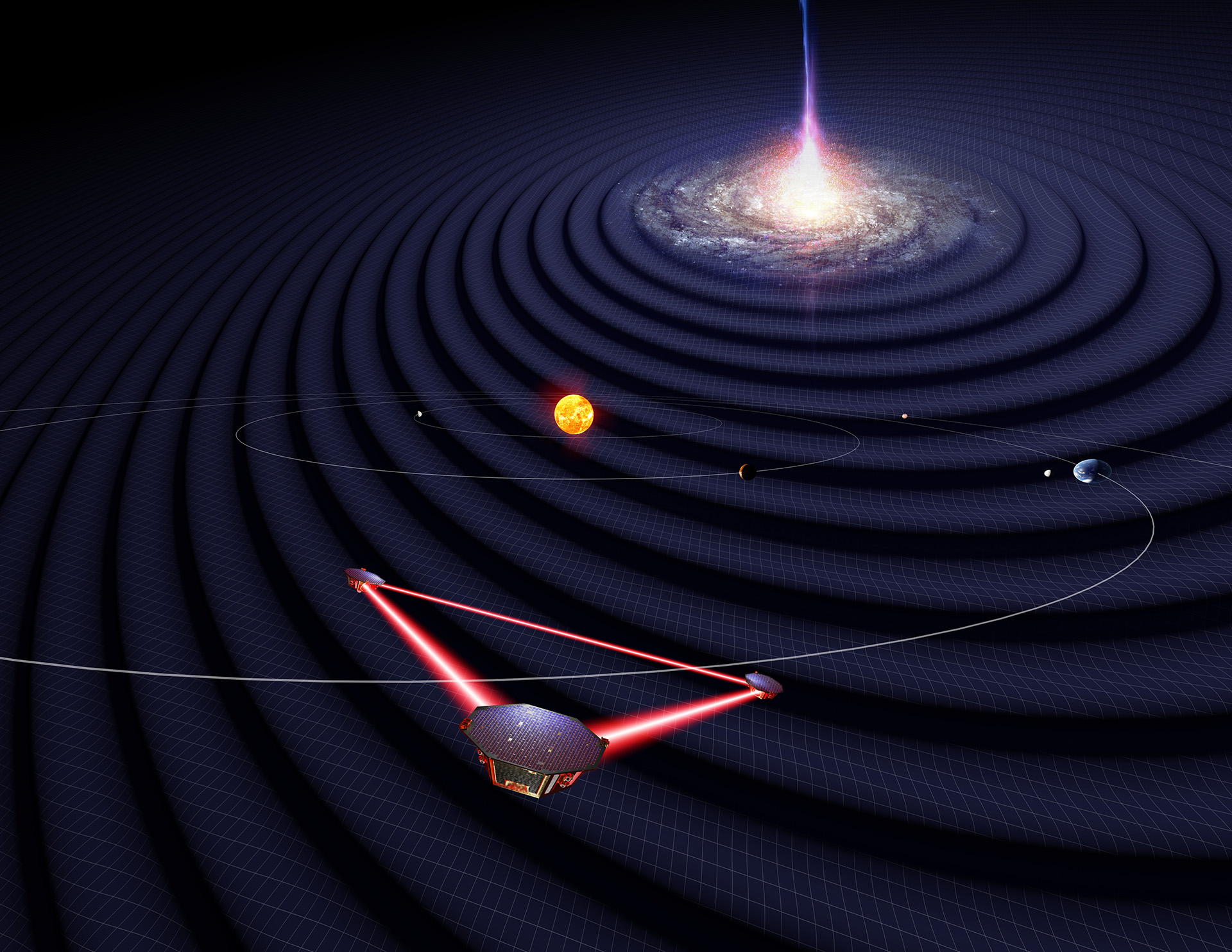
Observing gravitational waves in space with LISA
In 2035, the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is scheduled to be launched into space as a mission of the European Space Agency (ESA). It will observe previously inaccessible gravitational waves from a large range of new sources.
Chirping neutron stars
For some gravitational wave signals, one can go beyond graphs and animations – they can be made audible
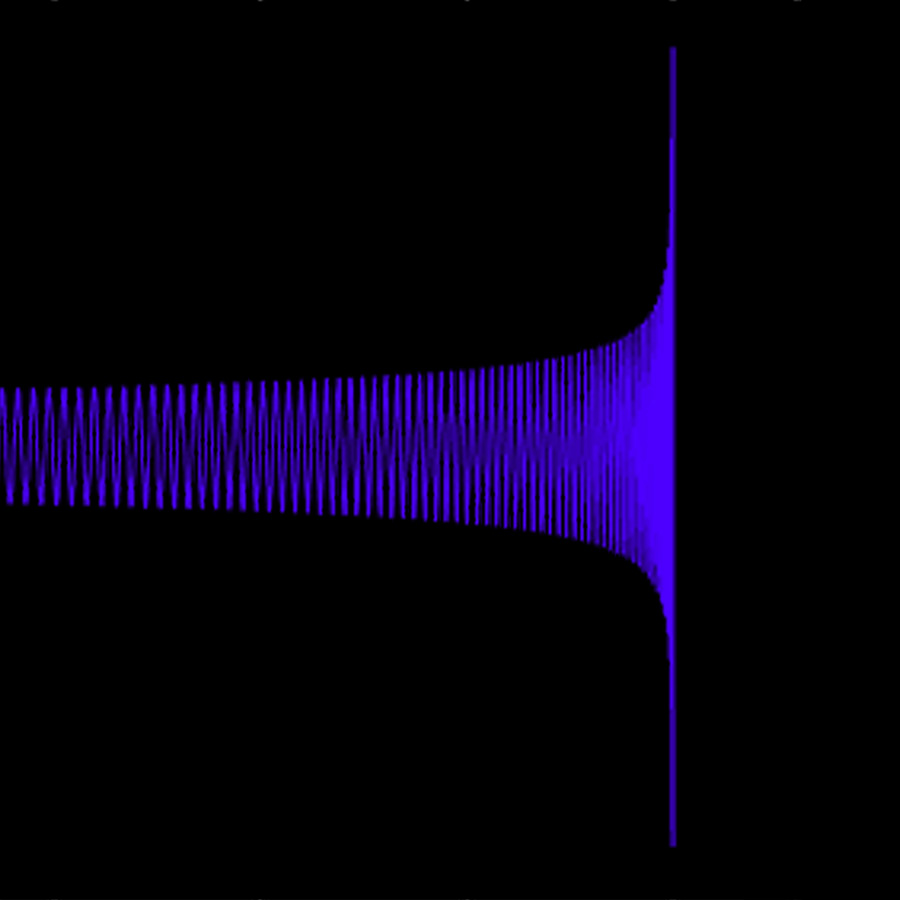
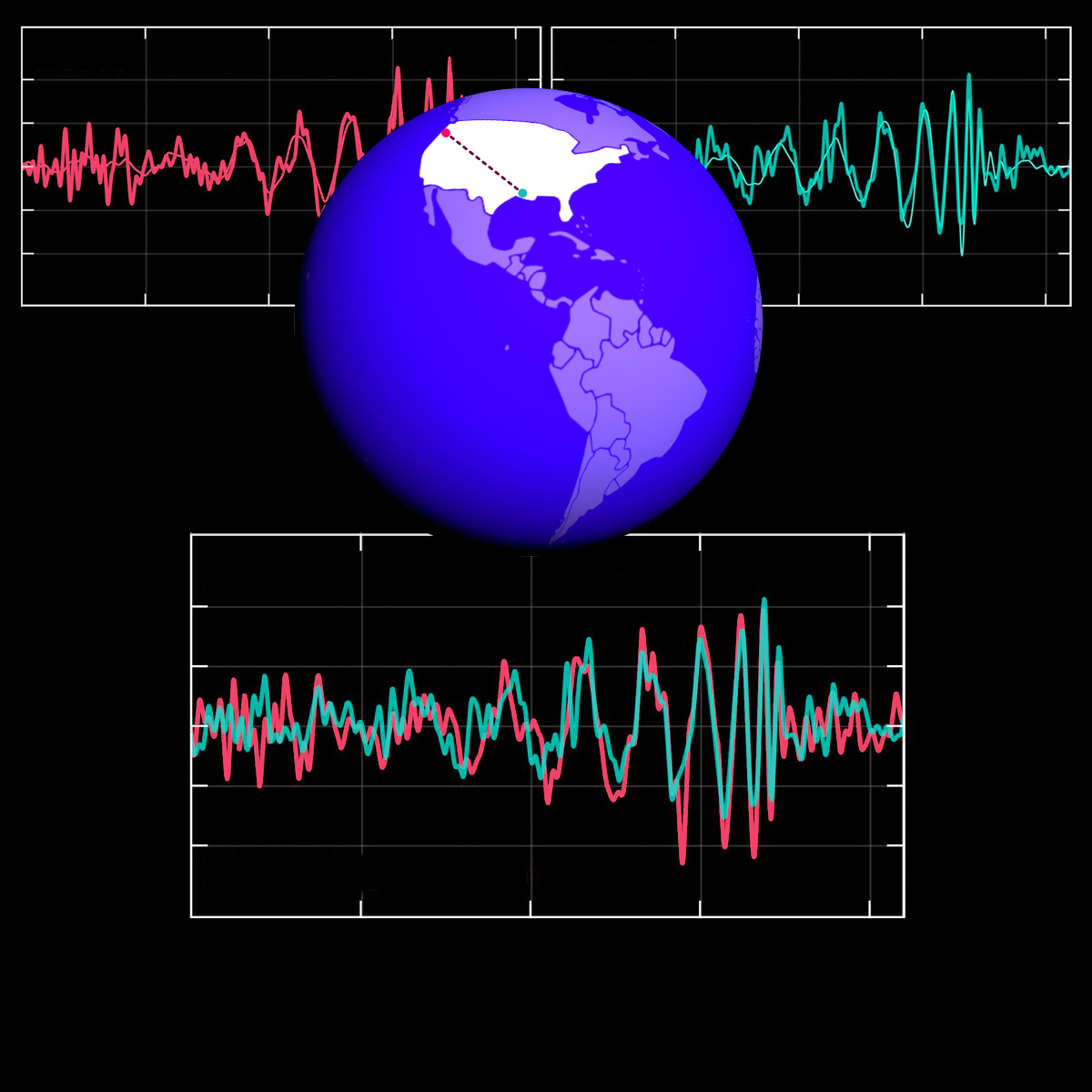
Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger
Albert Einstein predicted their existence back in 1916, and on 14 September 2015 they were directly detected for the first time: Gravitational waves. Two large interferometric detectors of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration with major contributions from German researchers detected the signal known as “GW150914”. The waves originate from the merger of two black holes and are the first direct observation of these exotic objects.
White Dwarf binaries as gravitational wave sources
White Dwarf binaries, their properties, and the role they will play for the planned space-borne gravitational wave detector LISA.